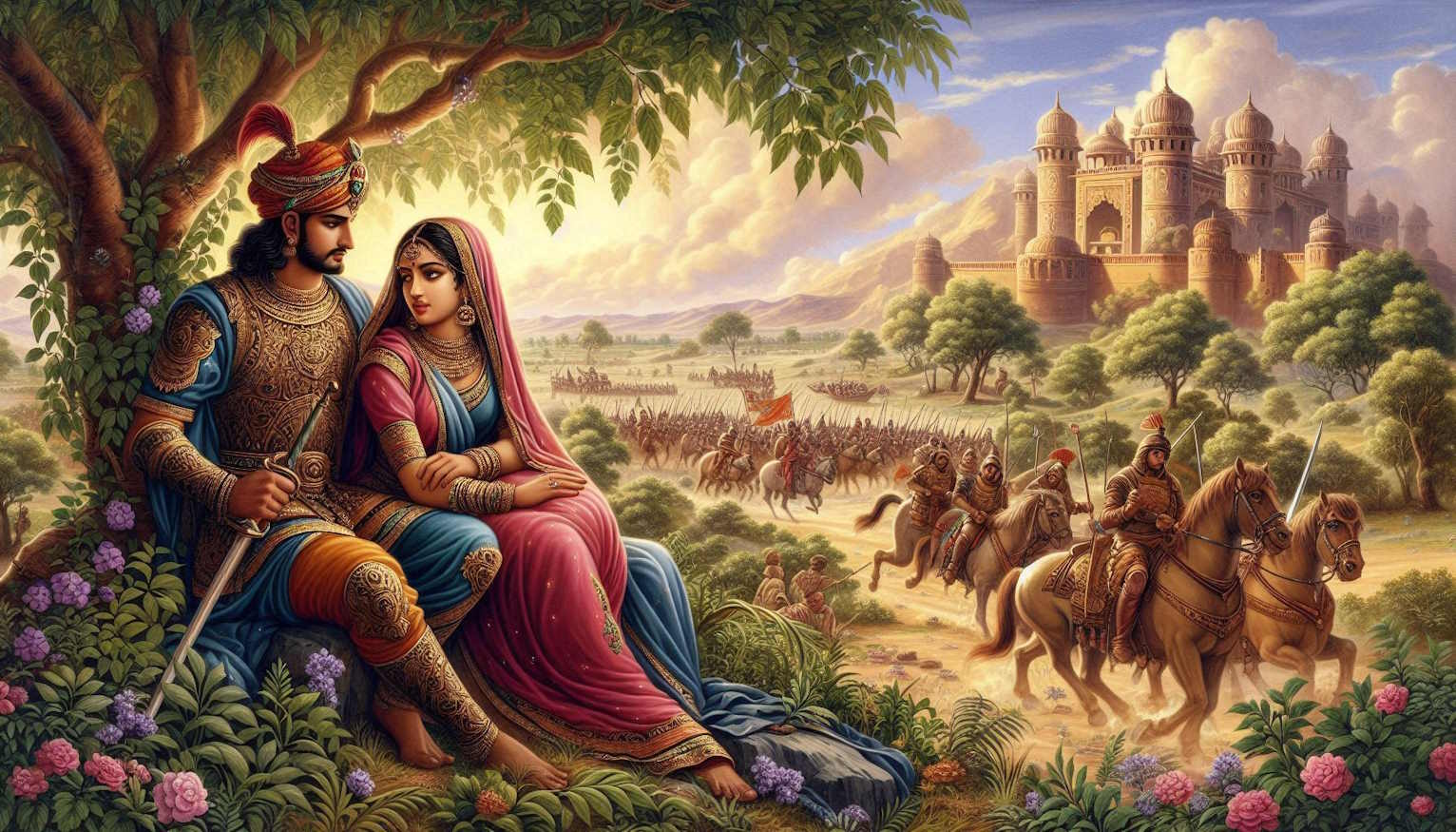
Khumman Raso is an epic poem from the 9th century, attributed to the poet Dalpat Vijay. It details the battles of Chittor’s ruler Khuman with the socio-political conditions of the age, and early forms of the Hindi language. The work is considered a significant piece of early Hindi literature, adding elements of Veer and Shringar Ras.
Khumman Raso: A book of 5 thousand Chhandas
Khumman Raso, a large book of five thousand ‘chhandas’, is well known in the tradition of Raso-books written in early ages of Hindi literature. Dalpati Vijay, a courtier poet in 9th century, is to be supposed to the author of this book. It is probably written in 9th century, as Acharya Ramchandra Shukla specify for being a descriptive anthology of battles performed by Chittor king Khumman in 9th century.
As this book chronologically mentions about kings up to Maharaja Raj Singh (King of Chittor during samvat 1752-1770), it is thought by some scholars (like Motilal Menariya and Agarchand Nahta) that Khuman Raso is a text written between Samvat 1730 to 1760. Because Khumman Raso is a chronological account of kings from Shri Rajachandra to Khuman, some scholars are of the view that possibly the original text might be firstly written in 9th century by a courtier poet Dalpati Vijay and descriptions of subsequent rulers in this text had been added by other courtier poets in different times up to 18th century.
Motilal Menariya does not assert Dalpati Vijay a contemporary of the Chittor-king Rawal Khumman. He suggests the name of a Jain-monk Dalpat Vijay to be the author of Khumman Raso, and indicates that Rawal Khumman depicted in this text was not a king, but ‘Khuman’ or ‘Khumman’ was a honorific title for Chittor rulers, that’s why the history from Bappa Rawal (First of Mewar Dynasty) to Maharana Sangram Singh II has been introduced in this large text.
The Text

Khumman Raso beautifully and largely describes battles(Yuddha), marriage, women with their secrets (Nayika-bhed), different seasons etc. and mainly focuses, as every raso text features, on Shringar (love and beauty) and Veer (bravery) Rasas . Doha, Savaiya, Kavitta etc. ‘chhandas’ are nicely used in this text. There are inputs of the poems of Prithviraj Rathaur, Sundardas, Bihari etc. of Reeti kal in between text, therefore it is proved that these inputs had been added in 18th century.
The Language
Language of Khumman Raso is Rajasthani and it is a successful poetic creation for its poetic beauty, language and style. Find an example from the text to appreciate the flow, simplicity and effect of the language and style-
“पिउ चित्तौड़ न आविऊ, सावण पहली तीज।
जोवै बाट विरहिणी, खिण-खिण अणवै खीज॥
संदेशो पिण साहिबा, पाछो फिरिय न देह।
पंछी घाल्या पींजरे, छूटण रो सन्देह॥”
The first ‘Teej’ (celebrated festival of women) has come, but my dearest, my beloved has not reached yet. ‘Virahini’ (a woman afflicted with the pain of being separated from her beloved) is still alive looking forward the way of his arrival spending every moment in anxiety and trouble. The beloved has sent the message to return soon but yet she is in hope, he will. That’s why the body is not being lifeless as she will she him with her. ‘Panchhi’ (the soul) is caged. It is doubt, it will get away from it. (As the message of the lover has been the hope for her meeting, the beloved being in trouble will not die for the hope of his coming is making her alive.)
Themes
The significant themes are as follows-
- Heroism and Valor: The epic poem celebrates the martial exploits and bravery of the Rajput ruler Khuman. It reflects the warrior ethos prevalent in Rajasthani society at the time.
- Romance and Chivalry: The work also delves into the romantic aspects of Khuman’s life, showcasing the ideals of love and chivalry.
- Cultural Reflection: The poem is a window into the 9th-century Rajasthani culture, offering insights into the social norms, practices, and the political landscape of the era.
Significance in the annals of Hindi Literature
- Linguistic Evolution: “Khumman Raso” is an important document for the study of early forms of the Hindi language, particularly Rajasthani Hindi. It showcases the evolution of language and poetic forms.
- Literary Heritage: The poem enriches the Rajasthani and Hindi literary heritage, standing as a testament to the storytelling and poetic traditions of medieval India.
- Historical Record: As a historical record, it provides historians and scholars with valuable information about the period’s socio-political conditions.